Heapsort is a fast sorting method based on heap data structure.
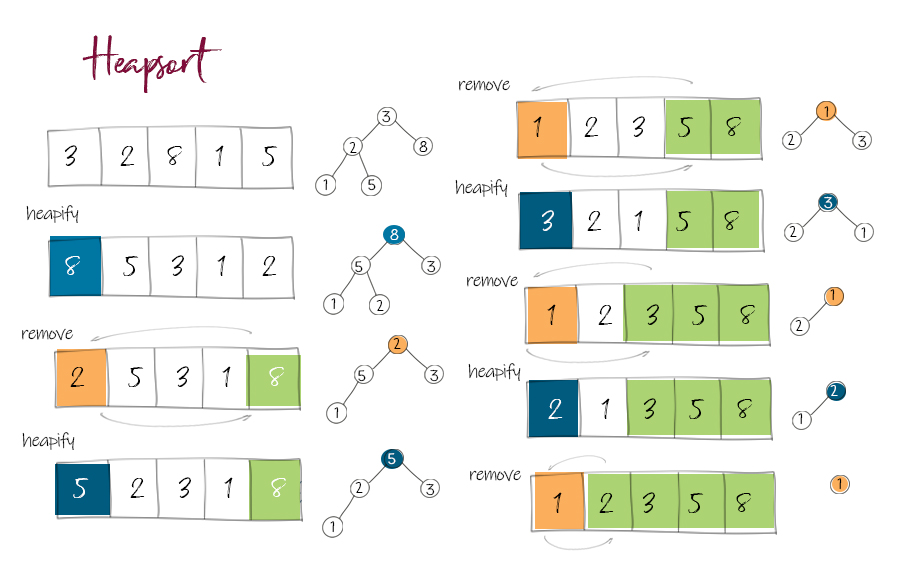
How heapify works in heapsort?
Heapsort uses a method “heapify”: you move the larger element in any subtree to the parent position. After heapifying, an array is turned into a heap data structure. The first element in the array is always the largest one.
Then you move the first element to the last position, and move the last one to the front. Run heapify again for the first (n-1) elements in the array. You get the second largest at the front. Move it to the second to last position. By repeating this process, you can get a sorted array. This is the idea of heapsort.
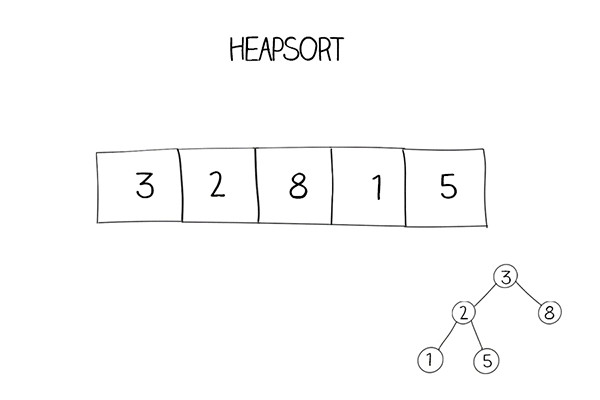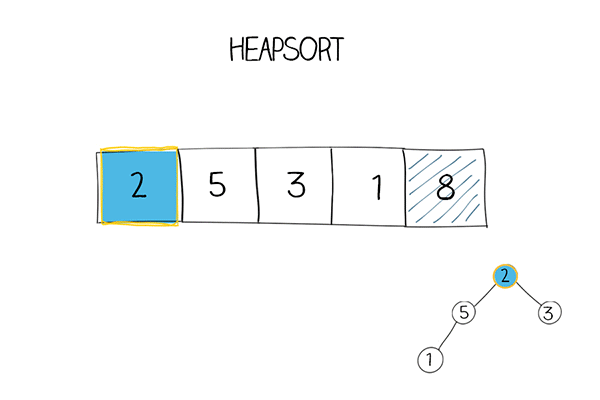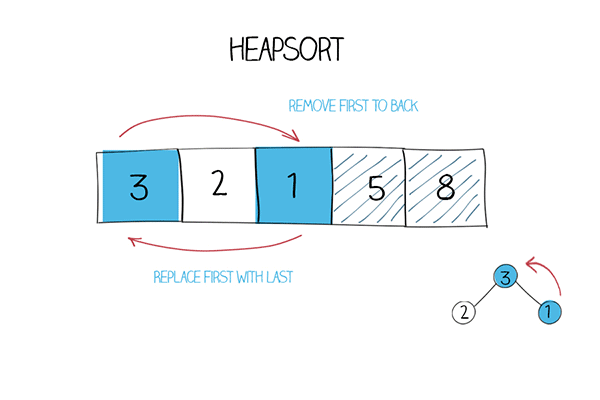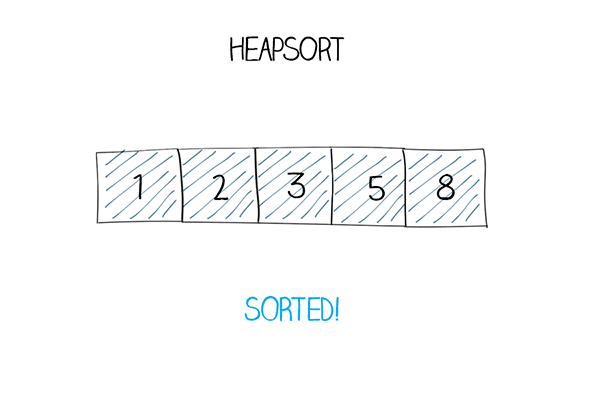
Iterative solution
The iterative solution uses remove and heapify methods. remove is to move the first element in the heap (the largest one) to the back of the array, and move the last to the front. Then call heapify. In heapify, a while loop starts from the root, compare the parent value with left and right child. Move the larger child to the parent position. Then move down to lower subtree to continue the process .
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | import java.util.*; public class HeapSort { //Solution 1, Iteration, Time O(nlogn), Space O(1) public static void heapSort(int[] a) { int n = a.length; for(int i = n/2-1; i >= 0; i--) {//make the array a max heap heapify(a, n, i); } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { //sort by remove the largest and put at the end int size = n-i-1; //new size after remove last a[size] = remove(a, size, i); //put the largest at the end } } //Remove the root from heap and heapify again, Time O(logn), Space O(1) public static int remove(int[] a, int size, int i) { int max = a[0]; a[0] = a[size]; //put last at front heapify(a, size, 0); return max; } //Max heapify, put larger at top, Time O(logn), space O(1) private static void heapify(int[] a, int size, int i) { int top = a[i]; int larger; while (i < size/2) { // from top down, swap with larger child int left = 2*i + 1; int right = 2*i + 2; if (right < size && a[right] > a[left]) larger = right; else larger = left; if (top >= a[larger]) break; a[i] = a[larger]; i = larger; } a[i] = top; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {19, 33, 4 , 61, 5, 38, -36, 21, 0}; heapSort(a); System.out.print("Heap sort (iteration): " + Arrays.toString(a)); } } |
Javascript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | //Solution 1, Iteration, Time O(nlogn), Space O(1) function heapSort(a) { var n = a.length; for(let i = parseInt(n/2-1); i >= 0; i--) {//make the array a max heap heapify(a, n, i); } for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { //sort by remove the largest and put at the end let size = n-i-1; //new size after remove last a[size] = remove(a, size, i); //put the largest at the end } } //Remove the root from heap and heapify again, Time O(logn), Space O(1) function remove(a, size, i) { var max = a[0]; a[0] = a[size]; //put last at front heapify(a, size, 0); return max; } //Max heapify, Time O(logn), space O(1) function heapify(a, size, i) { var top = a[i]; var larger; while (i < size/2) { // from top down, swap with larger child let left = 2*i + 1; let right = 2*i + 2; if (right < size && a[right] > a[left]) larger = right; else larger = left; if (top >= a[larger]) break; a[i] = a[larger]; i = larger; } a[i] = top; } let arr = [19, 33, 4, 61, 5, 38, -36, 21, 0]; heapSort(arr); console.log("Heap sort (iteration): " + arr); |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | #Solution 1, Iteration, Time O(nlogn), Space O(1) def heapSort(a) : n = len(a) for i in range(n//2, -1, -1):#make the array a heap heapify(a, n, i); for i in range(0,n) : #sort by remove the largest and put at the end size = n-i-1 a[size] = remove(a, size, i) # put the largest at the end #Remove the root from heap and heapify again, Time O(logn), Space O(1) def remove(a, size, i) : max = a[0] a[0] = a[size] # put last at front heapify(a, size, 0) return max #Max heapify, Time O(logn), space O(1) def heapify(a, size, i) : top = a[i] larger = 0 while i < size//2 : # from top down, swap with larger child left = 2*i + 1 right = 2*i + 2 if right < size and a[right] > a[left]: larger = right else: larger = left if top >= a[larger]: break a[i] = a[larger] i = larger; a[i] = top arr = [19, 33, 4, 61, 5, 38, -36, 21, 0] heapSort(arr) print("Heap sort (iteration): " + str(arr)) |
Recursive solution
In the recursive solution, heapify is a recursive function. It starts from the current position, ie the root of the subtree. Find the child which has the larger value. Swap the value with that child. Then calls itself with the position of the larger child.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | import java.util.Arrays; public class HeapSortRec { //Solution 2, Recursion, Time O(nlogn), Space (logn) public static void heapSort(int[] a) { int n = a.length; for (int i = n/2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {//make array a heap heapify(a, n, i); } for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) { //sort it swap(a, i, 0); heapify(a, i, 0); } } //heapify, recursion, Time O(logn), Space O(logn) private static void heapify(int[] a, int size, int i) { int larger = i; int left = 2*i + 1; int right = 2*i + 2; if (left < size && a[left] > a[larger]) larger = left; if (right < size && a[right] > a[larger]) larger = right; if (larger != i) { swap(a, i, larger); heapify(a, size, larger); //heapify again } } //Swap two elements by index, Time O(1), Space O(1) private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) { int tmp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = tmp; } public static void main(String args[]) { int[] a = {19, 33, 4 , 61, 5, 38, -36, 21, 0}; heapSort(a); System.out.print("Heap sort (recursion): " + Arrays.toString(a)); } } |
Javascript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | //Solution 2, Recursion, Time O(nlogn), Space (logn) function heapSort (arr) { var n = arr.length; for (let i = parseInt(n/2 - 1); i >= 0; i--) { // Build heap heapify(arr, n, i); } for (let i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) { swap(arr, i, 0); // swap with root heapify(arr, i, 0); // heapify again } } //Heapify, recursion, Time O(logn), Space O(logn) function heapify (arr, size, i) { let larger = i; let left = 2*i + 1; let right = 2*i + 2; if (left < size && arr[left] > arr[larger]) { larger = left; } if (right < size && arr[right] > arr[larger]) { larger = right; } if (larger != i) { swap(arr, i, larger); heapify(arr, size, larger); //heapify again } } //Swap two elements by index, Time O(1), Space O(1) function swap(arr, i, j) { let temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } let arr = [19, 33, 4, 61, 5, 38, -36, 21, 0]; heapSort(arr); console.log("Heap sort (recursion): " + arr); |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | # Solution 2, Recursion, Time O(nlogn), Space (logn) def heapSort(arr): n = len(arr) for i in range(n//2, -1, -1): # Build heap heapify(arr, n, i) for i in range(n-1, 0, -1): # sort arr[i], arr[0] = arr[0], arr[i] # Swap heapify(arr, i, 0) # Heapify # Heapify, recursion, Time O(logn), Space O(logn) def heapify(arr, size, i): larger = i left = 2 * i + 1 right = 2 * i + 2 if left < size and arr[i] < arr[left]: larger = left if right < size and arr[larger] < arr[right]: larger = right if larger != i: arr[i], arr[larger] = arr[larger], arr[i] #swap heapify(arr, size, larger) #heapify again arr = [19, 33, 4, 61, 5, 38, -36, 21, 0] heapSort(arr) print("Heap sort (recursion): " + str(arr)) |
Download and FAQ
Download heapsort in Java, JavaScript and Python
Merge sort
Sorting doodles compilation (YouTube)
What is heapsort space complexity?
There are two solutions for heapsort: iterative and recursive. Using iterative solution, no extra space is needed. The space complexity is O(1). Using recursive solution, since recursion needs memory for call stacks, the space complexity is O(logn). Therefore Iteration is more efficient.
What is heapsort time complexity?
Heapsort time complexity is O(nlogn). Heapsort is based on heap data structure. Since heap is a complete binary tree, the time complexity of heapsort is O(nlogn).